Why fermented foods need to be included in your diet
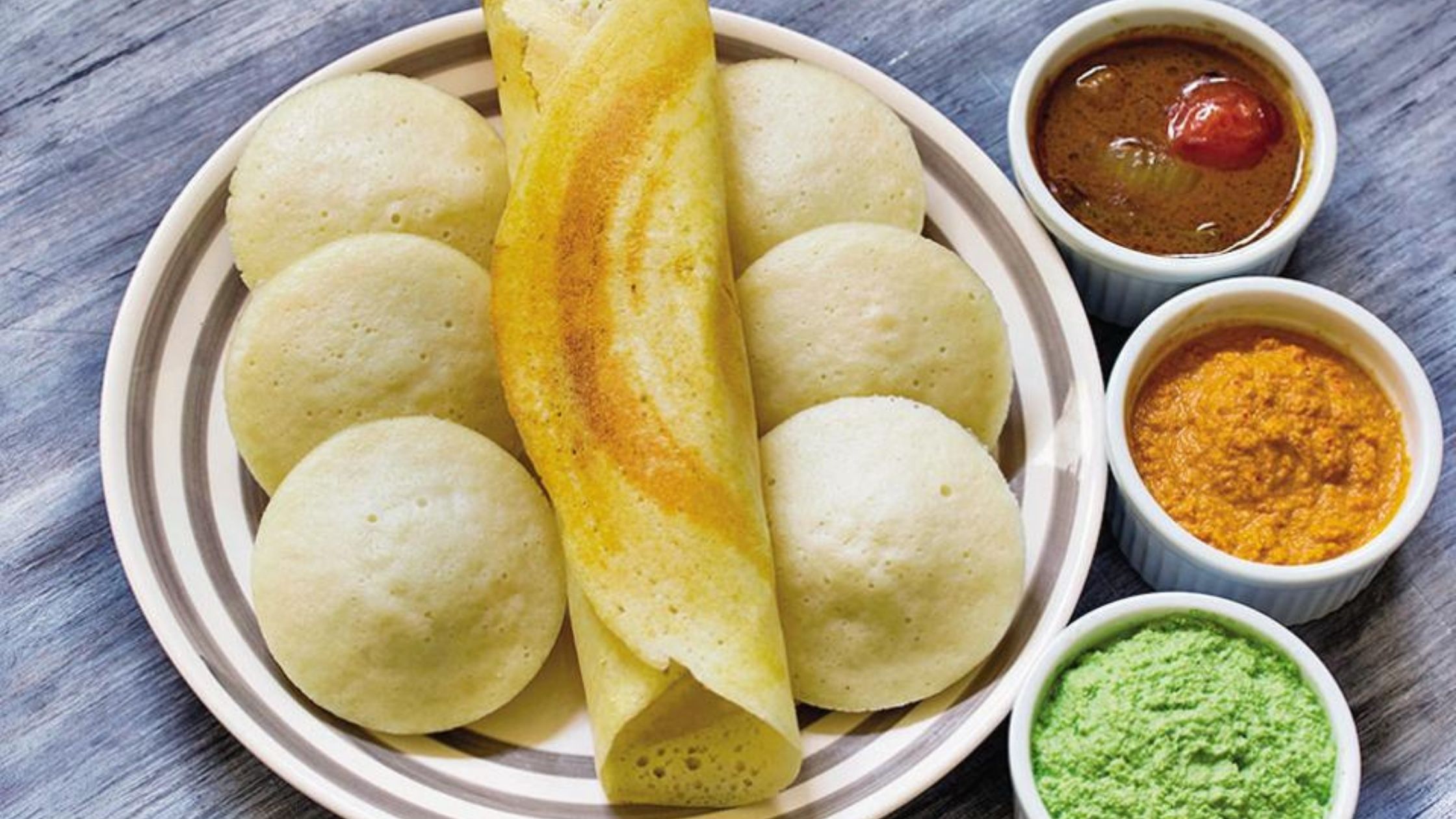

Foods that have undergone controlled microbial growth or undergone the process of fermentation are called fermented foods. Fermentation is an anaerobic process in which carbohydrates like starch/sugar is broken down by bacteria or yeast into organic acids, gases, or alcohol. Some of the fermented foods/beverages include idli, dosa, appam, dhokla, bread, kanji, wine, beer, etc.
Some of the benefits of fermented food include:
Reduced risk of diseases:
Fermentation reduces the risk of high blood pressure, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, obesity, increased cholesterol, and other inflammatory diseases. Fermented food is also found to have anticancer properties.
Improves digestion:
Fermented foods are known to improve gut immunity and reduce acidity or digestive issues. Probiotics or good bacteria named Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium are responsible for these benefits. A study conducted by Nourish Hoveyda in 2009 showed that the consumption of these foods helped reduce symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Fermentation also helps reduce symptoms of diarrhea, bloating, acidity, and constipation. Short-chain fatty acids produced in response to fermentation provide food for colonocytes thus helping in the maintenance of gastrointestinal health.
Improves immunity:
Fermented foods contain polyphenols that have antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects. There are studies linking fermentation to the stimulation of innate and adaptive immunity as well.
Reduces toxins in the food:
There is a reduction of toxins or anti-nutritional factors due to fermentation. Anti-nutritional factors block nutrients in food from getting absorbed. Some anti-nutritional factors include tannins, phytates, and enzyme inhibitors like trypsin or chymotrypsin.
Increases taste and palatability:
Fermented foods have increased taste and palatability. It can also be stored for longer periods of time without getting spoilt.
Improves nutrient availability:
Fermented foods can also enrich nutrient bioavailability, especially of vitamin B12. It is a good option for vegans who are usually deficient in this vitamin. Certain minerals like iron, zinc, magnesium, and calcium also become more bioavailable.